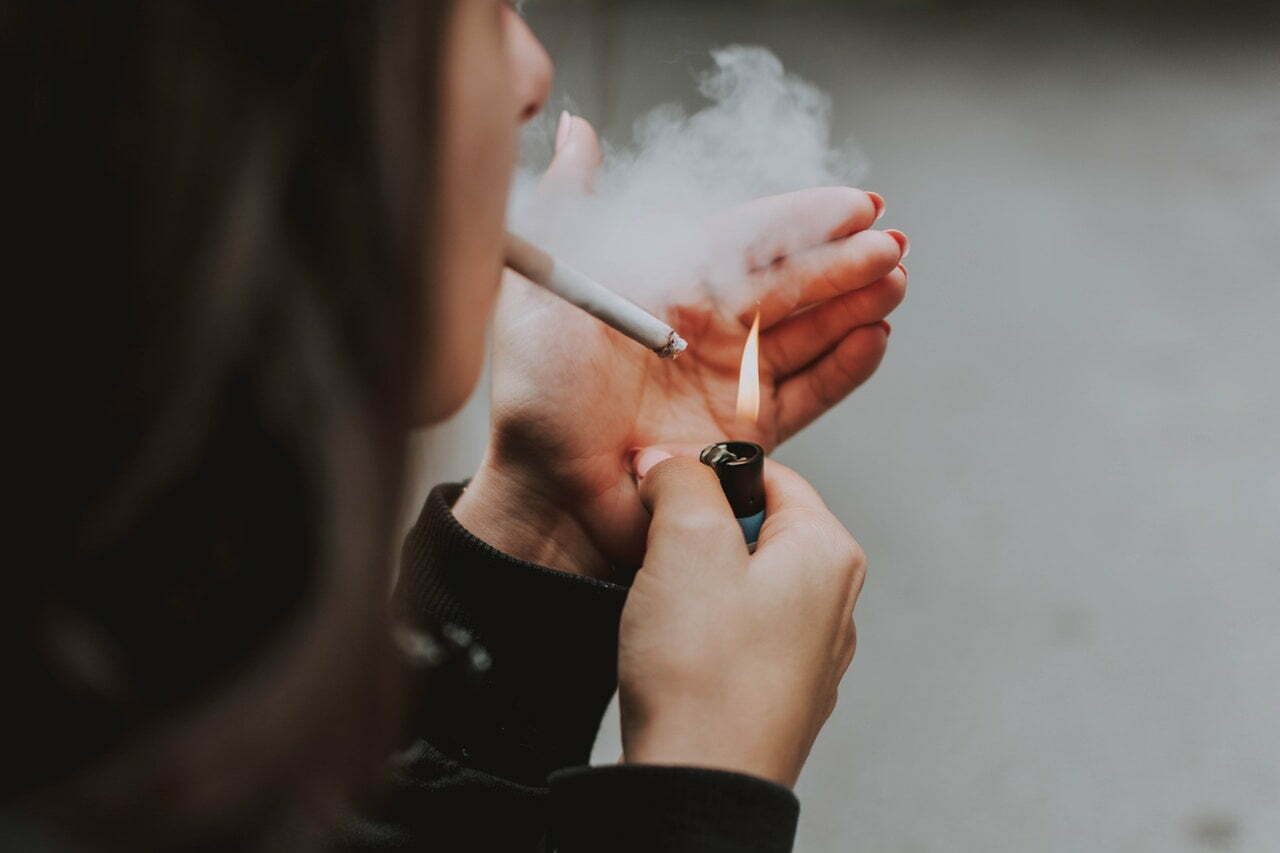
More than 6 dozen people die from abuse of opiates or heroin daily. In the United States, there are over 15 million alcoholics. Although addiction is a term most commonly associated with substances, such as drugs and alcohol, there are also other types of addictions related to behavior and impulse control, such as gambling and stealing. Individuals can also be diagnosed as sex addicts, workaholics or shopaholics. Why people develop addictions and how to identify those at risk has been the focus of medical research for decades.
Genetic Risk
A person’s genetic make-up can have a substantial impact on the choices that they make. Research has shown that genetics are a significant contributing factor in developing an addiction. You will not necessarily develop an addiction because you have a genetic predisposition. Lifestyle choices and other factors will also increase or decrease your chances of developing an addiction.
Family History
Your family’s history with addiction can indicate whether or not you are at risk. You may be more likely to become an addict if you have extended family members, such as a grandparent or uncle, who are addicts. However, you are more likely to develop an addiction if your parent is an addict. This may be partly because you have more genetic similarities with your parents. Exposure to addiction may also be a factor.
Addiction Triggers
People do not develop addictions solely because of genetics. People who are not genetically predisposed can still become alcoholics or drug addicts. Stress is one of the most common causes of addiction. When individuals are having marital problems or issues at work they may turn to alcohol or other substances to relieve their stress. This increases the risk of developing an addiction. Some people also develop an association between using or drinking and specific people or events. Learning to identify activities that prompt you to indulge your addiction can help you avoid common triggers.
Other Risk Factors
There are individuals who have memory disorders that contribute to their addiction. There is also evidence that brain chemistry can play a significant role in developing an addiction. Insufficient dopamine levels deprive individuals of pleasure. Drugs and alcohol trigger unusually high levels of dopamine in the body, which causes the addict to associate the substance with pleasure and fuels their addiction. Gender is also a factor. Men are more likely to develop an addiction than women.
Testing
Scientific advancements have linked specific genes with an increased risk of alcoholism or drug addiction. Individuals who are adopted or orphaned may be concerned about their potential genetic risk of developing an addiction. It is possible to be tested to determine if you have the genes that make you susceptible to substance addictions. The results do not guarantee you will develop an addiction.
Getting Treatment
You can’t change your genes but you can change your environment. Seeking treatment at reputable rehab clinics such as canadiancentreforaddictions.org is a way of removing yourself from known triggers. You will be educated about your addiction, learn to identify stressors that can cause relapse and develop strategies to decrease your risk of using substances again. Facilities like this also treat some addictions related to impulse control issues, such as gambling.
Preventing Addiction
Pursuing treatment can be a good strategy for preventing addiction. Having a genetic risk of addiction doesn’t mean you’re destined to become an addict. There are many other variables that are within your control that can mitigate those risks. Eliminating triggers and temptations and finding ways to manage stress are all ways to increase the likelihood that you will live an addiction-free life.
How Addiction Treatments Develop
Treatments for medical conditions can’t be perfected until the condition is cured. Due to the fact that researchers are still working to understand addiction and to identify all of the risk variables, there are ongoing advances in treatment plans. Various types of clinical trials are used to develop treatments for all medical conditions, including addiction. Addiction specialists focus on employing the most effective treatments identified. They also incorporate new treatment strategies when documented trials prove effective.